Arthrosis and arthritis are diseases in which the joints are affected.Because the names of these diseases agree, many people have thoughts about their identity.They perceive these terms as synonyms, suggesting that it is the same disease.However, arthrosis and arthritis are far from the same and there is a significant difference between it.To understand how different arthrosis is, let's understand what these diseases are.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a collective term that means inflammation of all joints and most often shows more extensive and serious pathological disorders in the body.That is, the disease is inflammatory and can impress both one and several joints.
There are a number of diseases that are accompanied by the development of arthritis:
- rheumatism;
- gout;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- psoriasis;
- Hemhramatosis.
In addition, there are reactive arthritis that develops as a result of complications after infectious diseases:
- influenza;
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- mycoplasmosis;
- Chlamida.
All these diseases are released into a separate group.
Inflammatory processes for arthritis mainly affect the synovial sheath and synovial fluid, causing disease (synovitis).As a result, the amount of this fluid increases, which is interpreted by the swelling of the affected joints.The cartilage that covers the surfaces of the bones is also inflamed, and over time the erosion that expresses the bone is formed on it.
What is arthrosis?
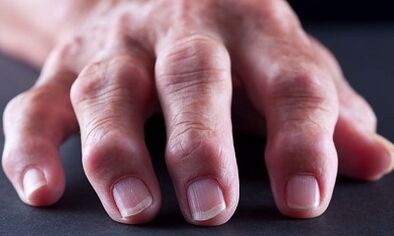
Arthrosis is a non -inflammatory dystrophic disease that is associated with deformity and destruction of cartilage tissue inside the joint.That is, pathological changes occur, which are manifested by dystrophy of cartilage lining of bone surfaces.Although sometimes it is a long -term inflammatory process that provokes thinning and damage to the cartilage.Arthrosis is often observed in the elderly as they carry cartilage tissue with age, as well as osteoporosis, which has a negative effect on the condition of the entire support and motor apparatus.
In some cases, arthrosis may occur at a young age in people who experience long joint loads.This category includes athletes, people suffering from obesity or persons whose professional activity leads to rapid wear and tear on the support and motor system.
The symptoms of the disease are caused by impaired cartilage function, as they are thinned and deformed, bone tissue grows, leading to the inability to fully perform depreciation and the friction of the bones that form the joint.As a result, the amount of synovial fluid is reduced, which must surround the joint surfaces.
Common causes of the development of arthrosis and arthritis
Because arthrosis and arthritis affect the joints and overall the entire maintenance motor is the motor apparatus, these diseases develop as a result of many factors.
Let's look at ten reasons that cause these diseases:
- hereditary factor;
- metabolic disorder;
- immune factor (especially for arthritis);
- congenital diseases of the connective and bone tissue;
- joint injuries;
- overweight, obesity;
- excessive physical activity;
- an unbalanced diet;
- hypothermia;
- Infections.
These are common causes that can cause both arthritis and arthrosis.But this is where their similarity ends.In addition, diseases only have differences.
Characteristic causes of the development of arthritis and arthrosis
Causing arthritis:

- Unbalanced, monotonous nutrition that causes impaired metabolic processes and immunity (poor nutrition provokes the development of infectious diseases, and their agents penetrate the synovial fluid and cause arthritis);
- strong joint hypothermia (overnight in the tent, bathing in cold water, poor poor shoes and clothes);
- any injuries (stretching, bruising or breaking);
- smoking and obesity;
- A sedentary lifestyle.
The causes of arthrosis:
- hereditary factor;
- old age;
- Injuries;
- Metabolic diseases.
Previously, the primary (when the cause of the disease is unknown) and the secondary (when the cause was known) the stage in the development of arthrosis.With the development of more modern diagnostic methods, the primary stage was called into question, since in all cases the main cause of the development of arthrosis is metabolic disorders in the form of carbohydrate metabolism and iron enzymes.Therefore, arthrosis may occur as a result of arthritis, since the dystrophy of synovial fluid is nothing more than a metabolic disorder.In the dystrophic processes, the blood circulation of the joint is impaired, which leads to the deterioration of the diet and the destruction of the cartilage.
What is the difference between arthritis from arthrosis
Let's look at how different arthrosis is.Because arthritis and arthrosis often affect the same joints, however, there is still some model in the location of the pathological process:
- Arthrosis often develops on large joints of the lower limbs (ankle, knee, hips).In addition, the pathological process develops in only one joint.Throughout their lives, all these joints experience very heavy loads, so it is not surprising that they wear and destroy due to destructive processes.Rarely, arthrosis affects the joints of the thumbs, hands and intervertebral joints.
- In arthritis, the joints are affected one by one, that is, the disease is characteristic of "flying".Suppose the wrist joint is inflamed for one day, on the other - the elbow, the third - the shoulder joint.In addition, several asymmetrical joints can be inflamed at once.
In addition to the characteristic localization of the pathological process, there is a difference between arthritis and arthrosis in symptoms:
- With arthritis, pain comes at night when one is at rest.And in the morning, patients experience a characteristic stiffness in the affected joints.In order to relieve stiffness, they must develop joints.Some patients interpret these phenomena as the norm, forgetting that healthy people do not need joint development after sleep.Their joints are always mobile and functional.With arthrosis, such stiffness is not observed.
- In the case of arthrosis, everything happens the opposite.At rest, the patient is relieved as the pain only occurs when it moves and becomes more intensive with significant motor activity.Sometimes with arthrosis, pain can also occur at night, but they are associated with the fact that the patient changes the position of the affected limbs in the sleep, which causes pain.
- The appearance of the joint with arthritis and arthrosis is also different.With arthritis, metacarpal phalax joints (convex bones of a compressed fist) swell and swell, blush and become hot (local temperature rises).With arthrosis, such symptoms are not observed, the joint seems absolutely normal.Of course, joint deformity may occur in the future as a result of osteophyte growth (joint growth), but even in this case there are no symptoms characteristic of arthritis.But with arthrosis there is a crisis in the affected joint, which is not with arthritis.
The general condition of patients in these diseases should be noted.With arthritis, in addition to joint pain, it experiences weakness, general disease: subfebrile temperature, chills, headache, loss of appetite, decreased body weight.With arthrosis, the problem is only in a non -functional and painful joint and the common symptoms are not observed.
It should be noted that arthritis often leads to arthrosis when the joint is destroyed and modified as a result of inflammation and its mobility is also impaired.However, inflammatory processes in the joints are observed with arthrosis.It is not so simple to understand the diagnosis that you need to understand the root cause of the development of these diseases.Arthritis, as a rule, occurs against the background of infections that have entered the joint tissue, and in the case of arthrosis, joint deformity occurs due to injury in the elderly.Of course, sometimes inflammation can join, but this does not always happen.
Differential diagnosis of arthrosis and arthritis
In order to understand what causes there was problems with the joint, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis.This diagnosis includes the following clinical tests:
- General blood test.
- General urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test;
- rheumatic tests;
- autoimmune norms (blood test for antibodies);
- X of the affected joints;
- study of synovial fluid;
- Radioisotopic scanning of the skeleton (in some cases);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Magnetic - resonance imaging (CT or MRI).
Blood test for arthritis and arthrosis
For adequate diagnosis of joint diseases, this procedure is mandatory and necessary.In the case of arthrosis, the clinical picture of the blood does not change at all, it can slightly increase the ROE (reaction to the settlement of erythrocytes) to 28-30 mm, usually with complications-synovitis.With arthritis, the blood count completely changes: leukocytes increase to 14,000, monitors the disposal of the leukocyte formula on the left, the reacting protein from the level C (CRB) and ROE to 40-80 mm increases.
C - a jet in the blood
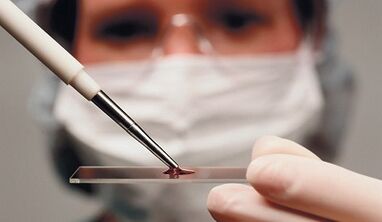
A biochemical blood test should be performed for differential diagnosis.In arthritis, there is an increase in inflammation of some immunoglobulins, seromucoid and C - reactive protein, which is not observed in arthrosis.The exact factor diagnosing the level of inflammatory process in joint disease is considered to be C - reactive protein (CRB).As the synovial fluid reacts with an increase in the protein to the occurrence of inflammation, with inflammatory and autoimmune processes in the body, its level increases to 10 mg/l and higher.Compared to healthy people whose reactive protein in the blood does not exceed 0.002 g/l.In this way, the increased level of reactive protein in the blood plasma eloquently shows the development of arthritis.
C - Reactive Protein (CRB) is a fast phase protein that is synthesized in the liver.Activates the body's immune response to the invasion of an inflammatory factor.After 24 hours the level of reactive protein in the plasma rises ten times.With adequate treatment, protein quickly reduces to normal indicators.With arthrosis in the patient's blood, the reactive indicators of the protein remain normal.
X -ray of the affected joints
This diagnostic method is the second most effective after clinical blood test.In this case, arthrosis is diagnosed precisely, since the degree of deformity of the bones along the width of the joint gap can be determined by the X -ray.For arthritis, this method is not significant, although it is certainly prescribed as a diagnostic technique.However, this method is imperfect because the degree of damage and destruction of cartilage tissue cannot be seen in the photo.
Differences in the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis
Arthritis and arthrosis have different causes and mechanisms of development, so their treatment is a little different.
In arthritis, it is necessary to first identify the cause of the development of inflammation and to neutralize it as soon as possible.If the onset of arthritis has an infectious etiology, then the patient is prescribed antibiotics.With the autoimmune origin of the disease, cytostatics and hormones are prescribed and gout arthritis requires a correction of uric acid in the body, therefore the treatment is performed by hypo -impaired drugs.
With arthrosis, treatment is aimed at restoring cartilage tissue and returning joint functions.Therefore, treatment is performed by chondroprotectors, hyaluronic acid, physiotherapy, sanitary treatment, massage and physiotherapy exercises.
Because both arthritis and arthrosis are accompanied by pronounced pain syndrome, non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs for internal and external use (tablets and ointments) act as painkillers with these diseases.Such drugs not only effectively eliminate pain, but also reduce the signs of inflammation.
Both conservative treatment and surgical therapy are used in the treatment of these diseases.It all depends on the level and scale of the joints.As a rule, this is the treatment of drugs and dentures.
As the very fact of chronic arthritis and the patient's arthrosis increases the likelihood of acute relapse, the therapeutic strategy should be aimed at preventing and preventing relapse.The following treatment is prescribed for this:
- The use of non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).Medicines in this group effectively eliminate the signs of inflammation, especially with arthritis, but are always included in the therapeutic complex and with arthrosis.
- The rapid elimination of muscle spasm that occurs in muscles adjacent to the joint.In this way, access to medicines, nutrients and oxygen is provided.
- Normalizing metabolic reactions.This is only possible after stopping the inflammatory process.
- Evacuation from the joint of uric acid salts (if we are talking about impaired metabolic processes).
- Normalization of acid - alkaline metabolism.
Modern medicine has been able to cure arthritis and arthrosis, but nevertheless, not every case of arthritis or arthrosis ends with complete success.
Success in the treatment of these diseases is to relieve inflammation of the joint and muscle spasm, in the normalization of the metabolic processes and the balance of the acid -alkaline.As a result of these actions, the joint begins to receive complete nutrition, oxygen and restoration of metabolic processes.
The recipes of traditional medicine are very effective in complex treatment of arthritis and arthrosis.Their use in this format is even approved by official medicine.It should be noted immediately that medicinal herbs are only an auxiliary agent in the fight against these disorders.Therefore, before continuing with folk remedies, you should be able to seek the doctor's recommendations.
Nutrition for arthritis and arthrosis
All joints of the joints, without exception, require a special nutritional nutrition.As the symptoms of arthritis affect the whole body, in some cases its course is complicated by serious disorders in the work of the heart, kidneys and liver, and arthrosis can immobilize the patient, lead to damage, and thus reduce the quality of his life, it is necessary to throw all the efforts to fight these diseases.

In the context of joint pathologies, the body should receive all the necessary nutrients, vitamins and minerals with certain addiction.The normalization of metabolic reactions and acid -alkaline equilibrium are paid attention to the products.
General diet recommendations can be as follows:
- Limit the consumption of red meat (pork, beef, lamb, deer, horses);
- rejection of products containing a large amount of fat and trans fat;
- complete rejection of alcohol;
- give preference to fish and seafood with low fat;
- Consume a large number of vegetables, fruits and herbs (in any form);
- Consumption of dishes based on cartilage: flood, jelly, jelly, marmalade;
- plentiful drinking mode;
- Take nutritional supplements with calcium, vitamins A, D and Group V.
General prevention of arthritis and arthrosis
In the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis, therapeutic strategy consists in preventing and preventing recurrence of arthritis and arthrosis.After all, the disease is easier to warn than for treatment.Therefore, the prevention of these diseases has the same principles:
- Avoid hypothermia of the legs (joints of the foot).After all, this time is the main thing in exacerbation of chronic diseases and infection with viral infections.
- Timely relief of chronic diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, bronchitis).
- Refusing uncomfortable high mill shoes.Unknown shoes create an additional load on the joints, leading to their destruction, deformity and dash and as a result of arthrosis.
- Fighting excess weight.Excess weight is a signal for metabolic disorders and arthritis almost always occurs against the background of such disorders.
- Moderate physical activity.Hard work puts pressure and load on the joint, resulting in their destruction and inflamed.
- Be sure to stick to a healthy lifestyle: often walk in the air, rest and eat, participate in physiotherapy exercises, see a doctor regularly.
Physical physical education for arthritis and arthrosis is a very important part of the therapy in a compartment with massage, diet therapy and physiotherapy.It provides inflamed joints with nutrients and oxygen and their recovery and recovery can not happen without this.

















































